
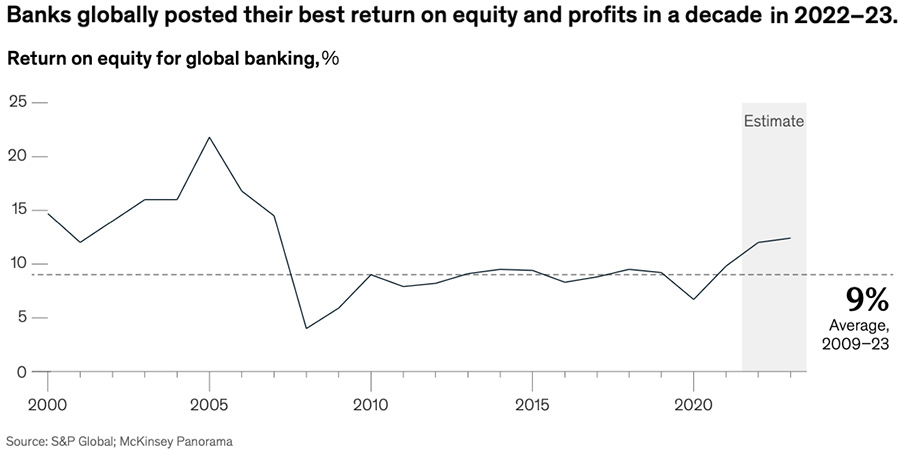
Banking profits are rising thanks to the increase of the interest rates settled by the central banks, even if this positive result come from a particular economic environment due to the necessity to decrease inflation. Despite the positive year, recently, banks have faced period of negative tax of interest, liquidity woes and failure of banks like the Californian Silicon Valley bank, one of the largest hi-tech start-up financiers, and Credit Suisse, a multi-secular Swiss bank acquired by UBS. For this reason, Banca d’Italia Governor, Fabio Panetta, recalled to remain vigilant and keep focusing on the long-term target. As a matter of fact, banks need to adopt new technologies and features and especially implement artificial intelligence to their process as well as developing digital infrastructure. The graph below shows that banks globally posted their best return on equity and profits in a decade.
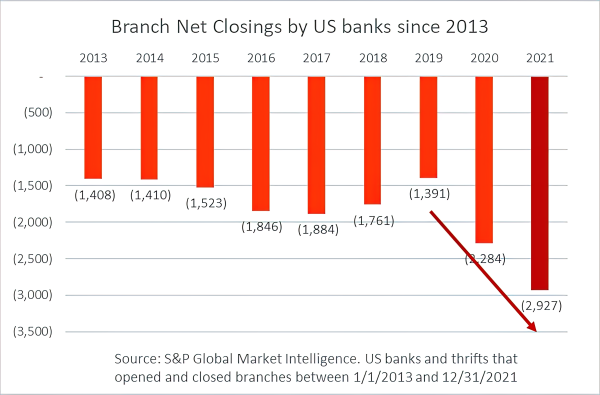
Let’s begin by analyzing some of the steps that banks are (taking), and which are the difficulties that they will face to stay competitive in the market. Starting from the most common phenomenon we can talk about the raising of digital branches and generally the use of home banking. The most spread-out trend at the moment is the need to have our personal bank on hand and without having to go to a just for carrying out everyday things like tracking our bank balance or trade stocks. The most prominent case in Italy is that of isybank, the digital bank created by Intesa San Paolo group, even if many all-digital banks already exist, in Italy, the biggest are Revolut and HYPE. They don’t have any branch and are operated entirely online. Below, the graph shows US banks and thrifts that opened and closed branches from 2013 to 2021.
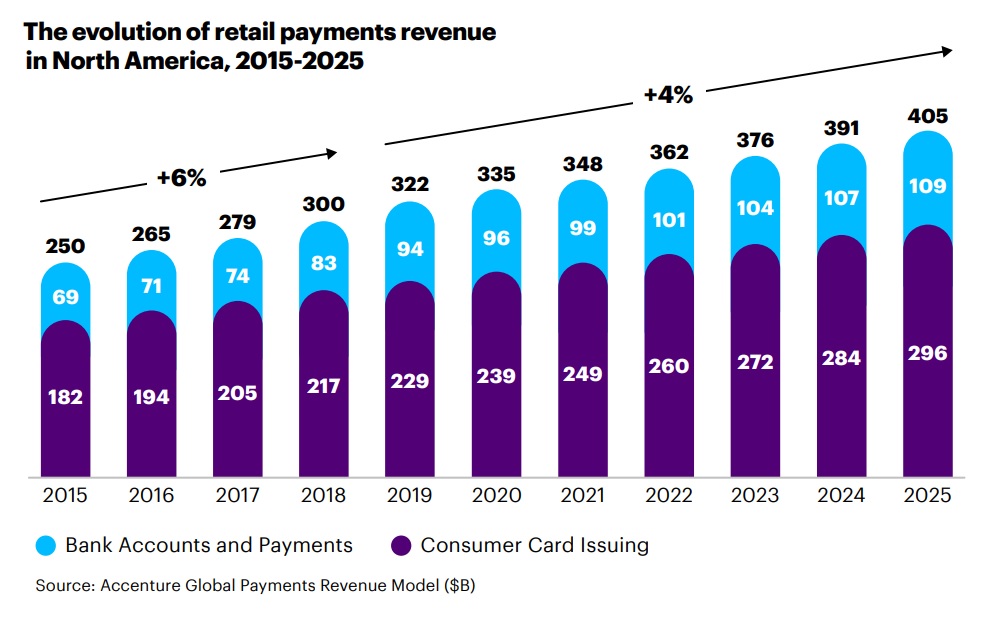
Another main theme is about the future of payments management, a growing market that could reach $2.9 trillion by 2030 and currently represents a large source of income for the banking system. Nevertheless, several reports show a decrease in profits by 2030 highlighting that something must change. The graph reported shows that the retail payment system is growing, even if credit card issuance turns out to be the one most used by consumers. The graph considers only North America, the most developed market.
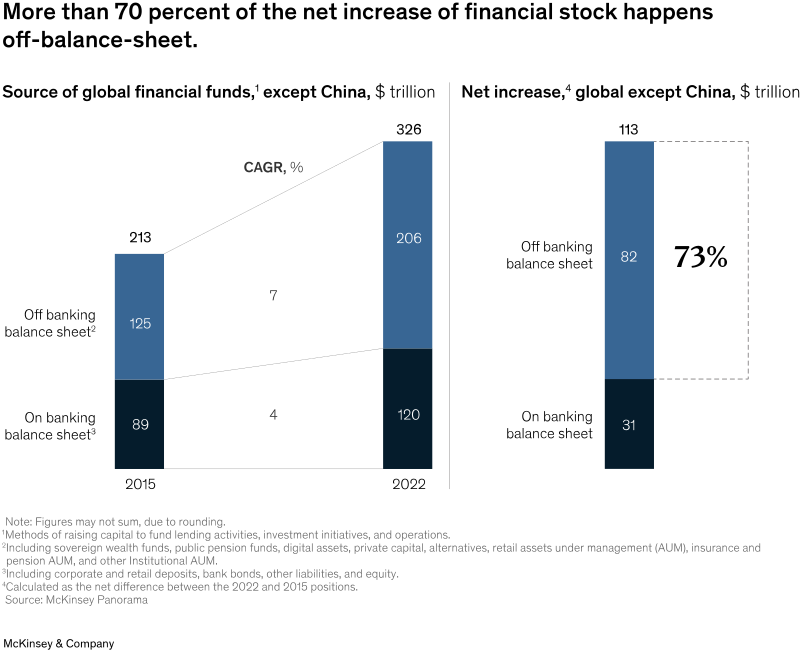
Finally, we also have to consider the trend among savers to allocate resources outside the traditional bank institution in search of higher returns. Therefore, the most risk-averse savers prefer to invest their saves in pension funds, mutual funds, insurance funds and other types of financial intermediaries. This comes from the fact that high level of inflation and high interest rates didn’t drive banks to reward clients as well as a period of negative rates before 2022. The following chart shows variations from 2015 to 2022.
Author: Luca Laurita
